India’s Agricultural Revolution Unveiled

The Roots of India’s Agricultural Revolution
India’s agricultural revolution began with the Green Revolution in the 1960s, shifting from traditional to modern agriculture. Innovations like high-yield crop varieties, chemical fertilizers, and expanded irrigation transformed India from a food-deficient country to a global agricultural leader.
Key Milestones in India’s Agricultural Journey
1960s-70s: The Green Revolution
- Introduction of high-yielding wheat and rice varieties.
- Increased use of chemical fertilizers and irrigation infrastructure.
1980s-90s: Diversification and Technology
- Shift towards horticultural crops and commercial farming.
- Adoption of agro-processing and farm mechanization.
2000s-Present: Focus on Sustainability
- Promotion of organic farming and climate-resilient agriculture.
- Integration of precision farming and digital tools.
Explore more about sustainable practices in our blog: India’s Sustainable Organic Farming Path.
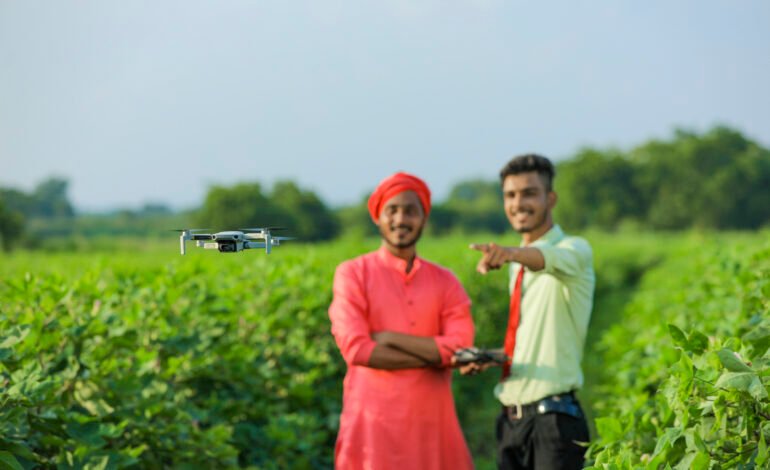
Technological Advancements Driving Change
Technology has been pivotal in India’s agricultural revolution:
- Precision Farming: Uses GPS and IoT to optimize resources.
- Biotechnology: Genetically modified crops for pest resistance and higher yields.
- Digital Platforms: Apps like Kisan Suvidha provide weather and market updates.
- AI and Machine Learning: For crop monitoring and pest detection.
Learn more about technological innovations in agriculture at the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
Sustainable Practices Shaping the Future
Sustainability is at the heart of modern agriculture:
- Organic Farming: Reduces chemical inputs for healthier produce.
- Water Conservation: Drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting improve efficiency.
- Agroforestry: Enhances biodiversity by integrating trees with crops.
Discover global sustainable agriculture initiatives on SARE.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
- Climate Change: Extreme weather impacts crop yields.
- Small Landholdings: Limits mechanization and scalability.
- Market Access: Farmers struggle with price volatility and distribution gaps.
Opportunities:
- Development of climate-resilient crop varieties.
- Formation of farmer producer organizations (FPOs).
- Expansion of agri-tech startups to address critical issues.
For more insights, check out our article: Overcoming India’s Farming Challenges.
Government Initiatives Supporting Growth
The Indian government is driving agricultural progress through various schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Protects farmers from crop losses.
- e-NAM (National Agriculture Market): Online trading for better price discovery.
- Soil Health Card Scheme: Promotes efficient nutrient use.
Explore these programs in detail at the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
The Road Ahead: Future of Indian Agriculture
Several trends are shaping the future of India’s agricultural revolution:
- Digitalization: Adoption of AI, IoT, and blockchain in farming.
- Vertical Farming: Urban agriculture to meet rising food demands.
- Agri-Tech Startups: Innovative solutions for productivity and sustainability.
For updates on emerging trends, visit the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI).
Conclusion
India’s agricultural revolution is driving progress, ensuring food security, and transforming the farming sector into a resilient and sustainable powerhouse. By embracing technology, sustainability, and government support, India is well-positioned to lead global agricultural innovation.