The Role of Digital Transformation in India’s Agriculture Sector
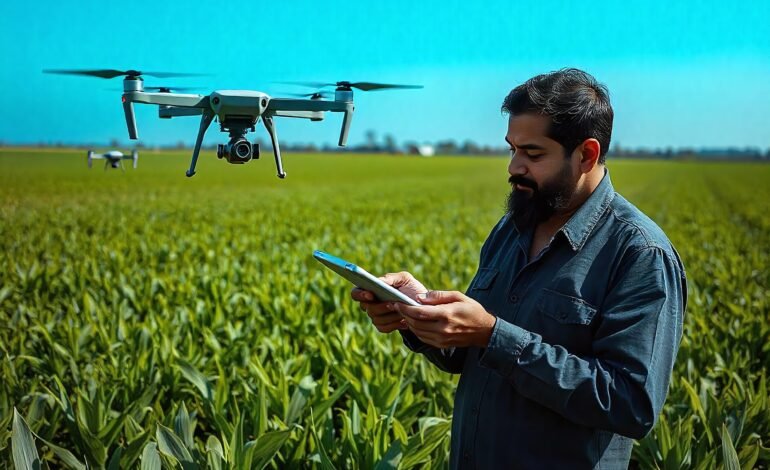

Introduction
Agriculture has always been the cornerstone of India’s economy, providing livelihood to millions of farmers. However, the sector has long faced challenges such as low productivity, water scarcity, unpredictable weather patterns, and inadequate market access. With the advent of digital transformation in Indian agriculture, technology-driven solutions are helping farmers increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance productivity.
Digital farming solutions, ranging from precision farming and smart irrigation systems to digital marketplaces for farm products, are revolutionizing agriculture in India. This blog explores the role of digital transformation in India’s agriculture sector and the opportunities it presents for farmers.
Key Drivers of Digital Transformation in Indian Agriculture
1. Precision Farming: Improving Efficiency with Data
Precision farming is one of the most significant digital advancements in agriculture. This approach involves using technology, data, and sensors to monitor and manage crops and soil. With the help of drones, IoT devices, and satellite imagery, farmers can gather real-time data on soil health, water content, and crop conditions.
Learn more about how the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare is supporting technology adoption in Indian farming.
By leveraging this data, farmers can make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, optimizing resource use and minimizing waste. This not only helps in boosting crop yields but also reduces the environmental impact of farming.
2. Smart Irrigation Solutions: Tackling Water Scarcity
Water scarcity is a growing concern for Indian farmers, especially in arid regions. Digital solutions like smart irrigation systems are helping address this challenge. These systems use sensors and real-time weather data to determine the optimal amount of water needed for crops. By automating irrigation schedules, farmers can conserve water while ensuring that crops receive the right amount of hydration.
For detailed insights into water management, check out the Water Resources Information System of India (WRIS).
These systems also help reduce water wastage, leading to improved water-use efficiency and sustainable farming practices. In water-stressed areas, smart irrigation is emerging as a game-changer.
3. Farm Management Software: Streamlining Operations
Farm management software is another key component of digital transformation in agriculture. These platforms allow farmers to track all aspects of farm operations, from planting schedules and weather forecasts to crop health and harvest tracking.
For instance, organizations like ICRISAT offer valuable resources on farm management best practices.
With a simple interface, farmers can plan and execute tasks efficiently, manage inventory, and even analyze financials. Some software solutions also offer predictive analytics, helping farmers anticipate market trends and adjust their operations accordingly.
4. Digital Marketplaces: Connecting Farmers to Consumers
Traditionally, farmers in India have faced challenges related to market access and fair pricing. Digital marketplaces are bridging this gap by providing a platform for farmers to directly sell their produce to consumers, wholesalers, and retailers.
Explore platforms like eNAM to see how digital marketplaces are revolutionizing agricultural trade.
These platforms offer greater transparency in pricing, eliminating the need for middlemen. Additionally, farmers can access a wider market beyond their immediate geographic location, improving their profitability and reducing post-harvest losses.
Opportunities for Farmers in the Digital Age
The digital transformation in Indian agriculture offers several opportunities for Indian farmers:
- Increased Productivity: Precision farming and better resource management through digital tools lead to higher crop yields and efficient farming practices.
- Cost Savings: Digital farming solutions help reduce the cost of inputs like water, fertilizer, and pesticides, which lowers overall expenses.
- Market Access: Digital marketplaces empower farmers by providing direct access to buyers and fair pricing for their products.
- Sustainability: Digital solutions help farmers adopt more sustainable farming practices, such as water conservation and reducing the use of harmful chemicals.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite the immense potential of digital transformation, challenges remain in the adoption of technology in agriculture:
- Digital Literacy: Many farmers in rural India lack access to digital literacy programs. Educating them on the use of digital tools is crucial for the success of these initiatives.
- Internet Connectivity: Poor internet infrastructure in remote areas hampers the ability of farmers to access digital solutions.
- Initial Investment: The cost of technology adoption can be a barrier, especially for small-scale farmers. Subsidies or low-interest loans for technology adoption can help mitigate this challenge.
As the government and private sector continue to invest in digital infrastructure, the future of agriculture in India looks promising. The continuous evolution of digital tools, combined with education and access to technology, will create a more prosperous, efficient, and sustainable agricultural sector.
Conclusion
Digital transformation in Indian agriculture is undoubtedly changing the face of farming. By embracing precision farming, smart irrigation, and digital marketplaces, Indian farmers are equipped to face the challenges of modern agriculture while increasing productivity, reducing costs, and improving sustainability. With the right support and infrastructure, the future of Indian agriculture can be more connected, efficient, and financially rewarding.
To learn more about ongoing initiatives in Indian agriculture, visit the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
As digital solutions continue to evolve, the Indian agriculture sector will continue to grow and innovate, ensuring that farmers remain at the forefront of this transformation.